Python 오라클 연결 cx oracle
DB CAFE
thumb_up 추천메뉴 바로가기
- DBA { Oracle DBA 명령어 > DBA 초급 과정 > DBA 고급 과정 }
- 튜닝 { 오라클 튜닝 목록 }
- 모델링 { 데이터 모델링 가이드 }
목차
1 아키텍처[편집]
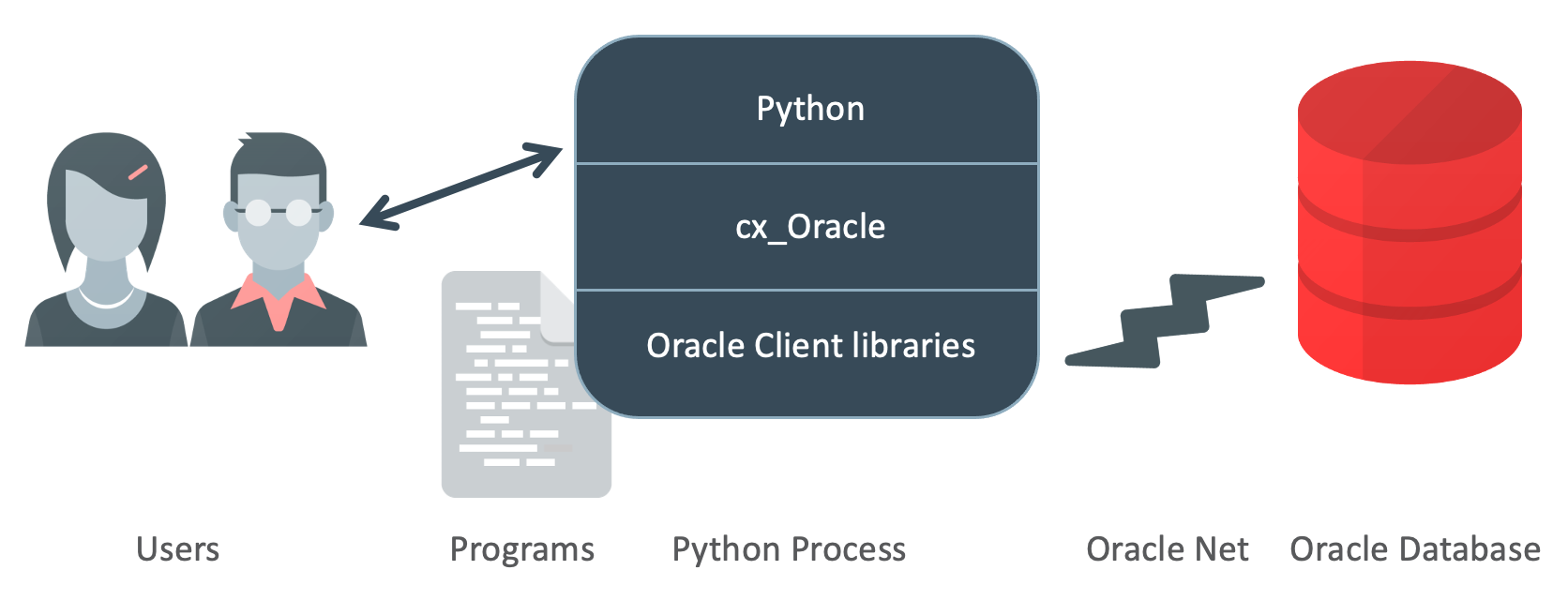
2 설치 / 설정[편집]
2.1 접속 모듈 설치[편집]
pip install cx_Oracle2.2 사용자 매뉴얼[편집]
https://cx-oracle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user_guide/sql_execution.html#fetch-methods
3 연결[편집]
3.1 접속 테스트[편집]
import cx_Oracle
#한글 지원 방법
import os
os.putenv('NLS_LANG', '.UTF8')
#연결에 필요한 기본 정보 (유저, 비밀번호, 데이터베이스 서버 주소)
connection = cx_Oracle.connect('Id','password','localhost/orcl')
# 오라클 버전 확인
print("Database version:", connection.version)
print("Client version:", cx_Oracle.clientversion())
# 커셔 연결
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute("""
select name
from test_db
where text = :texting""",
texting = "테스트"
)
for name in cursor:
print("테스트 이름 리스트 : ", name)
# 종료
cursor.close()
connection.close()3.2 커넥션 풀 사용하기[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import threading
import db_config
pool = cx_Oracle.SessionPool(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn,
min = 2, max = 5, increment = 1, threaded = True,
getmode = cx_Oracle.SPOOL_ATTRVAL_WAIT)
def Query():
con = pool.acquire()
cur = con.cursor()
for i in range(4):
cur.execute("select myseq.nextval from dual")
seqval, = cur.fetchone()
print("Thread", threading.current_thread().name, "fetched sequence =", seqval)
numberOfThreads = 2
threadArray = []
for i in range(numberOfThreads):
thread = threading.Thread(name = '#' + str(i), target = Query)
threadArray.append(thread)
thread.start()
for t in threadArray:
t.join()
print("All done!")3.3 DRCP 커넥션풀 사용하기[편집]
- 동시 접속이 많은 경우 DB 서버의 자원이 금방 고갈될 수 밖에 없는 문제를 해결하기 위해 보통은 WAS (Web Application Server) 차원에서 커넥션풀을 만들어서 DB접속풀 공유하면서 사용하는 것이 일반적임.
import cx_Oracle
import threading
pool = cx_Oracle.SessionPool(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn + ":pooled",
min = 2, max = 5, increment = 1, threaded = True,
getmode = cx_Oracle.SPOOL_ATTRVAL_WAIT)
def Query():
con = pool.acquire(cclass = "PYTHONHOL", purity = cx_Oracle.ATTR_PURITY_SELF)
cur = conn.cursor()
for i in range(4):
cur.execute("select myseq.nextval from dual")
seqval, = cur.fetchone()
print("Thread", threading.current_thread().name, "fetched sequence =", seqval)
numberOfThreads = 2
threadArray = []
for i in range(numberOfThreads):
thread = threading.Thread(name = '#' + str(i), target = Query)
threadArray.append(thread)
thread.start()
for t in threadArray:
t.join()
print("All done!")4 조회 / 패치[편집]
4.1 fetchone() 함수를 사용하여 1건 패치[편집]
- 로우갯수가 많을때 fetchall() 함수는 너무 많은 메모리
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
cur.execute("select * from dept order by deptno")
row = cur.fetchone()
print(row)
row = cur.fetchone()
print(row)4.2 fetchmany() 사용하여 다건 패치[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
cur.execute("select * from dept order by deptno")
res = cur.fetchmany(numRows = 3)
print(res)4.3 Scrollable cursors[편집]
- 스크롤 가능한 커서를 사용하면 응용 프로그램이 쿼리 결과에서 앞뒤로 이동할 수 있습니다.
- 행을 건너뛰고 특정 행으로 이동하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor(scrollable = True)
cur.execute("select * from dept order by deptno")
cur.scroll(2, mode = "absolute") # go to second row
print(cur.fetchone())
cur.scroll(-1) # go back one row
print(cur.fetchone())cur.scroll(1) # go to next row
print(cur.fetchone())
cur.scroll(mode = "first") # go to first row
print(cur.fetchone())4.4 프리패치[편집]
- Python 프로그램으로 각 일괄 처리에서 반환되는 행 수를 늘려 쿼리 성능을 개선하는 방법
- 행을 미리 가져오기 및 배열 가져오기는 모두 데이터베이스로의 왕복을 줄이기 위한 내부 버퍼링 기술입니다.
- 차이점은 버퍼링을 수행하는 코드 레이어와 버퍼링이 발생하는 시기입니다.
import cx_Oracle
import time
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
start = time.time()
cur = con.cursor()
cur.prefetchrows = 100
cur.arraysize = 100
cur.execute("select * from bigtab")
res = cur.fetchall()
# print(res) # uncomment to display the query results
elapsed = (time.time() - start)
print(elapsed, "seconds")
4.5 바인드 변수 사용하기[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
sql = "select * from dept where deptno = :id order by deptno"
cur.execute(sql, id = 20)
res = cur.fetchall()
print(res)
cur.execute(sql, id = 10)
res = cur.fetchall()
print(res)5 바인딩 입력 처리[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
rows = [ (1, "First" ), (2, "Second" ),
(3, "Third" ), (4, "Fourth" ),
(5, "Fifth" ), (6, "Sixth" ),
(7, "Seventh" ) ]
cur.executemany("insert into mytab(id, data) values (:1, :2)", rows)
# Now query the results back
cur2 = con.cursor()
cur2.execute('select * from mytab')
res = cur2.fetchall()
print(res)6 에러 처리[편집]
6.1 배치 에러[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
# 예를 들어 6 이 중복입력 되어 유니크 제약 조건 오류가 발생된경우
rows = [ (1, "First" ), (2, "Second" ),
(3, "Third" ), (4, "Fourth" ),
(5, "Fifth" ), (6, "Sixth" ),
(6, "Duplicate" ),
(7, "Seventh" ) ]
cur.executemany("insert into mytab(id, data) values (:1, :2)", rows, batcherrors = True)
for error in cur.getbatcherrors():
print("Error", error.message.rstrip(), "at row offset", error.offset)
# Now query the results back
cur2 = con.cursor()
cur2.execute('select * from mytab')
res = cur2.fetchall()
print(res)
</python>
The other data gets inserted and is queried back.
에러가 발생된 값을 제외 하고 모두 입력된다.
또한 커밋 이나 롤백 처리를 할수 있다.
* 커밋처리 시
<source lang=sql>
con.commit()- 롤백처리 시
con.rollback()7 LOB 처리[편집]
7.1 CLOB 조회[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
print("Inserting data...")
cur.execute("truncate table testclobs")
longString = ""
for i in range(5):
char = chr(ord('A') + i)
longString += char * 250
cur.execute("insert into testclobs values (:1, :2)",
(i + 1, "String data " + longString + ' End of string'))
con.commit()
print("Querying data...")
cur.execute("select * from testclobs where id = :id", {'id': 1})
(id, clob) = cur.fetchone()
print("CLOB length:", clob.size())
clobdata = clob.read()
print("CLOB data:", clobdata)7.2 CLOB 문자열 처리[편집]
import cx_Oracle
import db_config
con = cx_Oracle.connect(db_config.user, db_config.pw, db_config.dsn)
cur = con.cursor()
print("Inserting data...")
cur.execute("truncate table testclobs")
longString = ""
for i in range(5):
char = chr(ord('A') + i)
longString += char * 250
cur.execute("insert into testclobs values (:1, :2)",
(i + 1, "String data " + longString + ' End of string'))
con.commit()
def OutputTypeHandler(cursor, name, defaultType, size, precision, scale):
if defaultType == cx_Oracle.CLOB:
return cursor.var(cx_Oracle.LONG_STRING, arraysize = cursor.arraysize)
con.outputtypehandler = OutputTypeHandler
print("Querying data...")
cur.execute("select * from testclobs where id = :id", {'id': 1})
(id, clobdata) = cur.fetchone()
print("CLOB length:", len(clobdata))
print("CLOB data:", clobdata)